Day 2 :
Keynote Forum
Nallusamy Sivakumar
Sultan Qaboos University, Oman
Keynote: Production of ethanol from pretreated waste paper through separate enzymatic hydrolysis and fermentation
Time : 10:00-10:40

Biography:
Nallusamy Sivakumar has expertise in microbial fermentation. His areas of research interests are enzyme production, bioenergy, biofuel and bioprocessing, He is working on the possible utilization of different waste materials as alternative, cheap and renewable substrates for the production of microbial enzymes and other value added products. He established the bioprocess lab in Sultan Qaboos University and supervising the team of students working in bioprocessing. He is also working on bioactive compounds. In this, he is concentrating on the effect of different plant extracts and their essential oils on pathogenic bacteria and their possible mode of action. He also has a long teaching career,
Abstract:
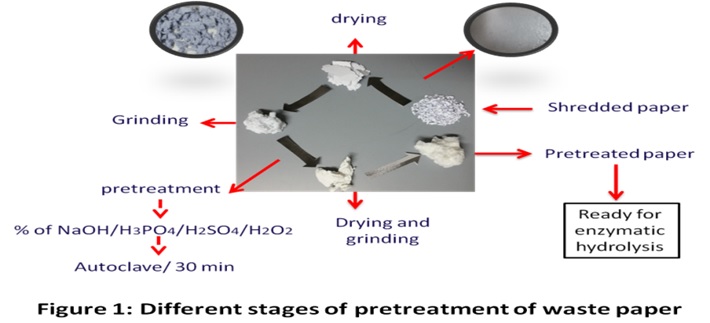
Waste paper is considered as one of the major components of municipal and industrial wastes and has the potential to be used as an excellent alternative feedstock for ethanol production. In this study, the effect of various pretreatments on efficient hydrolysis of waste office paper and newspaper into sugars and subsequent production of ethanol through fermentation was studied. The shredded papers were soaked in deionized water (5 % w/v), milled and dried at 60° C for 24 h. The dry matter was then milled again to remove most physical barriers of cellulose structure. The prepared waste papers were subjected to various pretreatments using sulphuric acid, phosphoric acid, sodium hydroxide and hydrogen peroxide at a concentration of 0.1, 0.5 and 1% (v/v). Pretreatment with H2O2 (0.5 % v/v) at 121°C for 30 min was considered as the most effective method as it increased the available cellulose, produced a high sugar yield, high delignification and less inhibitors formation. The effect of single (37 FPU/g solids) and two enzyme mixture (37 FPU + 25 CBU/g solids) was carried out using 2% (w/v) solid loadings. The solid loadings experiment was done by loading 1-4% (w/v) solids with 37 FPU + 25 CBU/g solids of enzyme loadings. The enzymatic hydrolysis of pretreated office paper and newspaper with 3% solid loadings resulted in the sugar yield of 23.48 and 13.12 g/L with hydrolysis efficiency of 91.8 and 79.6 %, respectively. Further, the hydrolysates of office paper and newspaper were used as a substrate to produce ethanol through fermentation using Saccharomyces cerevisiae resulted about 11.15 and 6.65 g/L with the productivity of 0.32 and 0.28 (g ethanol/L/h), respectively. Thus, the improved yields achieved through the pretreatment with 0.5% H2O2 and subsequent ethanol production suggested that the wastepaper could be used as a potential feedstock for bioethanol production.
Recent Publications:
- Al-Siyabi B, Gujarathi AM, Sivakumar N (2017) Harmonic Multi-objective Differential Evolution Approach for Multi-objective Optimization of Fed-Batch Bioreactor. Materials and manufacturing processes http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/ 10426914. 2017.1279308.
- Annamalai N, Sivakumar N (2016) Production of polyhydroxybutyrate from wheat bran hydrolysate. Journal of Biotechnology 237: 13–17.
- Aishwarya R, Sivakumar N, Reginald V (2016) Fish waste-Potential low cost substrate for bacterial protease production: A brief review. The Open Biotechnology Journal 10: 335-341.
- Sivakumar N, Al Zadjali A, Al Bahry S, Elshafie A and Eltayeb EA (2016) Isolation and characterization of cellulolytic Bacillus licheniformis from compost. African Journal of Biotechnology 15: 2434-2446.
- L-Kharousi M, Sivakumar N, Elshafie A (2015) Characterization of cellulase enzyme produced by Chaetomium sp. isolated from books and archives, Eurasian Journal of Biosciences 9: 52-60.
Keynote Forum
Aurangzeb Akram
Imperial College London, UK
Keynote: Production of ethanol from pretreated waste paper through separate enzymatic hydrolysis and fermentation
Time : 11:00-11:40

Biography:
Engr. Dr. Aurangzeb Akram is performing academic research in the Department of Chemical Engineering and Chemical Technology Imperial College London United Kingdom, Department of Chemical and Biochemical Engineering, Technical University of Denmark (DTU), Denmark, NFC Institute of Engineering and Technology Pakistan and the Institute of Chemical Engineering and Technology Faculty of Engineering and Technology University of the Punjab Pakistan and pursuing his career in academics, research and government advisory services. He is performing reviews and publishing of research work for peer-reviewed international scientific journals and is a member of different international scientific societies. Award lecture is a communication about the latest development in the field of renewable energy, membrane technology, biomass, bioreactor engineering and environmental biotechnology processes. His research interest is on the topics of energy and fuels, environmental sustainability and the relevant treatment processes and performing research on novel membrane based bioengineering design for carbon decontamination of industrial and municipal effluents for discharge into fresh water streams using anaerobic consortium producing biofuel.
Abstract:
High strength wastewaters including effluents from distillery, brewery, sugar and maize products industries require treatment before discharge into aquatic environment. For carbon decontamination of food and beverage industries effluents, membrane bioreactors are being developed to decouple the solid retention time from the hydraulic retention time (HRT) and to produce solids free better quality effluents while the use of anaerobic biomass reduces the cost of excessive sludge disposal and produces methane as a source of renewable energy1. Three litres submerged anaerobic membrane bioreactor (SAMBR) was used to study the effects of organic shock loads in the form of step change in feed strengths and alkalinity to different magnitudes (two and five times) at constant HRT to obtain an insight into microbial responses and chemical oxygen demand (COD) removal performance. The SAMBR was able to handle the high sludge loading rate (0.8 gCOD gVSS-1 l-1) and the organic loading rate (9.6 gCOD l-1 d-1) with 90 % COD removal at high gas sparging rate (3m-3 m-2 h-1) due to a uniform shear force. Settled and attached growth biomass inside SAMBR at low gas sparging rate (1.2 m-3 m-2 h-1) survived an organic shock load of 20 gCOD l-1 (five times the steady state concentration) both in the presence and absence of moderate sodium toxicity (4.5 gNa+ l-1)4. Acetate and propionate were the two most significant volatile fatty acids (VFAs) appeared at high substrate concentration, whereas butyrate appeared only at relatively low pH. Formate appeared for biomass acclimatised for above neutral pH and disappeared at low pH for similar flocs morphology3. Substrate degradation depends upon active biomass and not on flow regime inside the bioreactor. However VFAs and soluble microbial products (SMPs) retention at low shear conditions (1.2 m-3 m-2 h-1) confirm the concept of electrostatic “gel layer” formation2. Based on the results of the specific methanogenic activity using batch assays a larger amount of methane production potential is observed in SAMBR at higher loading rate.
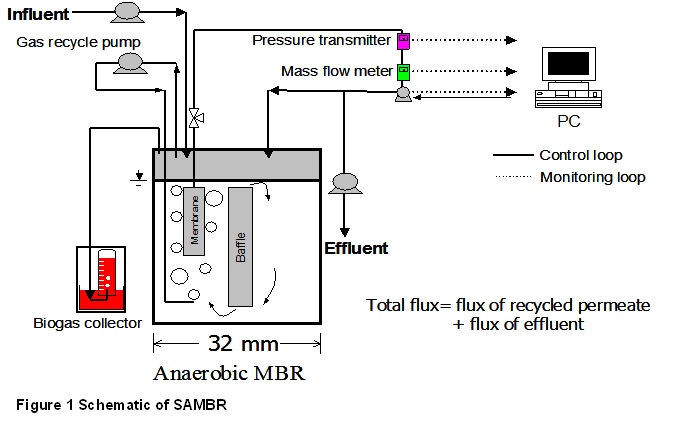
Figure: Schematic of SAMBR
Key words: Membrane bioreactor, organic loading rate, sludge loading rate, sodium toxicity, gel layer, renewable energy.
Recent Publications:
- Al-Siyabi B, Gujarathi AM, Sivakumar N (2017) Harmonic Multi-objective Differential Evolution Approach for Multi-objective Optimization of Fed-Batch Bioreactor. Materials and manufacturing processes http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/ 10426914. 2017.1279308.
- Annamalai N, Sivakumar N (2016) Production of polyhydroxybutyrate from wheat bran hydrolysate. Journal of Biotechnology 237: 13–17.
- Aishwarya R, Sivakumar N, Reginald V (2016) Fish waste-Potential low cost substrate for bacterial protease production: A brief review. The Open Biotechnology Journal 10: 335-341.
- Sivakumar N, Al Zadjali A, Al Bahry S, Elshafie A and Eltayeb EA (2016) Isolation and characterization of cellulolytic Bacillus licheniformis from compost. African Journal of Biotechnology 15: 2434-2446.
- AL-Kharousi M, Sivakumar N, Elshafie A (2015) Characterization of cellulase enzyme produced by Chaetomium sp. isolated from books and archives, Eurasian Journal of Biosciences 9: 52-60
